ИННОВАЦИОННАЯ ПОЛИТИКА ВЬЕТНАМА ДЛЯ РАЗВИТИЯ ПОТЕНЦИАЛА В СФЕРЕ ЭТНИЧЕСКИХ МЕНЬШИНСТВ В ПЕРИОД 2021-2030
Научная статья
Дао Тхи Ай Тхи *
Национальной академии государственного управления, Ханой, Вьетнам
* Корреспондирующий автор (daoaithi93[at]gmail.com)
Аннотация
Каковы элементы и инновационная политика правительства Вьетнама для развития потенциала чиновников в районах проживания этнических меньшинств? Цель этого исследования состоит в том, чтобы сосредоточиться на двух факторах, которые считаются особенно важными: 1) приверженность политических лидеров целям развития потенциала должностных лиц в районах проживания этнических меньшинств и 2) институционализация, которая означает более эффективное осуществление инновационной политики для развития потенциала чиновников в районах проживания этнических меньшинств.
Работа базируется на теоретических и качественных методах исследования, и содержит обсуждения, посвященные государственной инновационной политике для более эффективного проникновения приверженности правительства в бюрократию и соответствующих реформ, которые бюрократия ввела в форме новых организаций, новых компетенций и нового режима работы. Из чего следует создать правовую базу для развития потенциала чиновников в районах проживания этнических меньшинств.
В этом исследовании также делается попытка объяснить, почему эта та же административная система начала проявлять все более серьезные ограничения по мере того, как страна приближалась к новой цели, и как правительство Вьетнама пыталось перестроить свою административную систему, чтобы приспособиться к этой новой среде миссии.
Для достижения этой цели в документе рассматриваются некоторые из следующих моментов: 1) Разъяснение концепций и характера инновационной политики для повышения потенциала должностных лиц в районах проживания этнических меньшинств; 2) Схема структуры для инноваций и содействия социально-экономическому росту в районах проживания этнических меньшинств; 3) Предложение инновационной политики для повышения потенциала чиновников в районах проживания этнических меньшинств в период 2020-2030 гг.
Ключевые слова: инновационная политика; развитие потенциала; должностные лица; этнические меньшинства.
VIET NAM’S INNOVATION POLICY FOR CAPACITY DEVELOPMENT OF OFFICIALS IN ETHNIC MINORITY AREAS IN THE PERIOD OF 2021-2030
Research article
Dao Thi Ai Thi *
National Academy of Public Administration, Hanoi, Vietnam* Corresponding author (daoaithi93[at]gmail.com)
Abstract
What are the elements and innovation policies through the Vietnamese government to develop the capacity of officials in ethnic minority areas? The goal of this study is to focus on two factors being considered particularly critical: 1) commitments of political leaders to the objectives of capacity development of officials in ethnic minority areas, and 2) institutionalization means to more effectively implement innovation policies to develop capacity of officials in ethnic minority areas. Based on theoretical research methods, by qualitative methods, the article contains discussions focusing on government innovation policy for more effective penetration of government’s commitment into the bureaucracy and the corresponding reforms that the bureaucracy introduced in the form of new organizations, new competencies, and new mode of operations. From which to create a legal framework for developing officials’ capacity in ethnic minority areas. This study also makes its attempt to explain why this same administrative system started to manifest increasingly more serious limitations as the country approached a new goal and how the Vietnamese government tried to restructure its administrative system to adapt to this new mission environment. To achieve this goal, the paper addresses some of the following points: 1) Clarifying the concepts and nature of innovation policies to improve the capacity of officials in ethnic minority areas; 2) Scheming framework for the capacity to innovate and promote socio-economic growth in ethnic minority areas; 3) Proposing innovation policies to improve the capacity of officials in ethnic minority areas in the period of 2020-2030.
Keywords: innovation Policy; Capacity development; Officials; Ethnic minority areas.
I. Introduction and Literature reviewThe lack of qualified officials has long been such the barrier and challenge for ethnic minorities in Vietnam, which causes instability, lack of sustainable development of ethnic minorities. The objective of capacity development for ethnic minority officials is to develop comprehensive capacities in terms of knowledge, attitudes and skills related to the job positions of each cadre, based on respect for law and civil servant ethics.
The demands of social life in ethnic minority areas are increasing day by day, the problem of developing capacity of officials in civil service activities in ethnic minority areas is rather difficult and complicated. The relationship between civil servants and people of ethnic minorities in a certain angle has not brought satisfaction to the parties involved in public administrative relations. That situation is part of the weakness and incompetence of civil servants in ethnic minority areas [5].
When Vietnam joined the World Trade Organization, integrating intensively and extensively into the world economy, to enhance the development competitiveness in the international arena, it is crucial more than ever that the capacity of the public team Ethnic minorities need to be raised one step. In order to have a contingent of ethnic minority civil servants who are good at both professional and proficient skills, especially leadership and management skills, the government is in need to have innovative strategies with appropriate strategic levels with development requirements of Vietnam.
The capacity of civil servants in ethnic minority areas is different from the capacity of civil servants in general, which is affected by the characteristics of ethnic minority areas including: (1) Vietnam has 54 ethnic minorities, many different customs and practices, so there must be different ways of leadership and management in accordance with the cultural characteristics and practices of each ethnic group; (2) Extreme geographical and natural conditions; (3) The development of ethnic minorities is uneven, the economy is underdeveloped with persistent poverty; (4) Educational level is still low, there still exists numerous useless customs; (5) Common practice of shifting cultivation of wandering hill tribes; (6) A place with great potentials for natural resources; (7) Being a border length with other countries, it should be a strategic position in terms of politics, security and defense. In Vietnam, places called ethnic minorities are home to more than 50% of ethnic minorities people [5].
With these characteristics, it is required that cadres must have specific characteristics such as knowledge of psychology and emotions of ethnic minority people, knowledge of ethnic minority languages, and perception of documents, their practices, case management skills, interpersonal skills, leadership skills, appropriate management skills, etc.
The Vietnamese officials in ethnic minority areas are those who are recruited or appointed to hold a regular duty, classified according to the level of training and specialty, classified into a rank or rank of job position in system of State administrative agencies in ethnic minority areas performing the state management functions [8].
Therefore, the government should have specific policies different from leaders and managers in other places, to the general requirements of civil servant capacity, there also should be specific requirements for the capacity of ethnic minority officials, then according further specific innovation policies on attracting, recruiting, training, fostering, appointing, remuneration, etc., as appropriate.
The Government of Vietnam needs to answer the following two questions: (1) What is the capacity frame for officials of ethnic minority areas? (2) What solutions does Vietnam need to innovate policies for developing capacity of ethnic minority officials?However, there has not been any study by any author about the innovation policy for developing the capacity of ethnic minority officials in Vietnam. Hence, the author chose this topic for her research. The paper focuses on: (1) The pathway of capacity building among ethnic minority officials and the impact of the government’s innovative policies; (2) Solutions to innovative policies to develop the capacity of ethnic minority officials.
II. Results and discussion
1. The pathway of capacity building among ethnic minority officials and the impact of the government’s innovative policies
Ethnic minority officials’ capacity is a chain related to the orderly arrangement and coordination of many different processes and actions. The basis for forming capacity of officials is through the government’s innovative policies to create opportunities for staff education, training and practical experience. The education and training must be purposeful, organized and suitable to the specific objectives and circumstances of management activities in ethnic minority areas. [2]
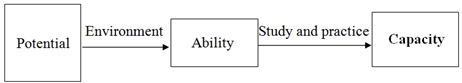
Fig. 1 – The capacity development path is described as follows:
– Potential: Being hidden in every individual, potential does not become an ability without favorable environment. Discovering human potential is to create an environment conducive to development potential. In order for the potential to develop into ability, there must be an environment, especially the environment of government policies.– Ability: one step higher than the potential, there are signs of “positiveness” of a capacity if there is a good environment and opportunity. The ability to become an ability needs to be studied, trained and worked. In order for the ability to develop into capacity, the cadres themselves must make efforts to study and practice. – Capacity: is the sum of emotions, attitudes, emotions – knowledge, perceptions, knowledge – practice, skilled and artistic actions. A comprehensive capacity of staff is the key to effective management of government in ethnic minority areas.
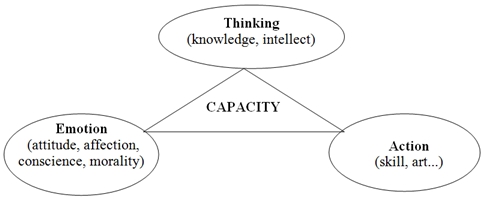
Fig. 2 – Capacity constituent elements
- The thinking capacity of ethnic minority civil servants is composed of factors: knowledge, understanding, analysis, synthesis, application and evaluation.
- The emotional capacity of public servants in ethnic minority areas is constituted by the following factors: perception, value, nature, attitude, and affection.
- The capacity of action of civil servants in ethnic minority areas is constituted by the following factors: imitation, initiative, skills, techniques and arts.
The policy of innovation for officials capacity development can be perceived as the State interventions creating that creative potential, favorable institutional environment. Through the study of secondary documents in Vietnam, the author discovered gaps of existing policies including: (1) lack of training and retraining policies for ethnic minority officials; (2) lack of policies to rotate ethnic minority officials to workplaces; (3) lack of incentive policies, encouraging innovation and management technology innovation for officials of ethnic minority areas; (4) Lack of policies to monitor personal responsibilities, etc. Especially, there is an absence of innovative policies in technology transfer, scientific achievement transfers into socio-economic development of ethnic minority areas. The insufficiency of innovation policy will influence the long-term economic growth of some regions and countries [1]. As the OECD put it: “A major driver of economic growth and rising living standards in the post-World War II period was rapid advances in technological capacity and trade”[3]. Commerce estimates that technological innovation in general and management technology innovation in particular have contributed to 75% of the growth of the US economy since World War II. In a highly accredit study of 98 developed and developing countries, Klenow and Rodriguez-Clare claims that up to 90% of the increase in per capita income is generated by innovation. creation [4].
III. Formulating innovative policies to officials capacity development in ethnic minority areas to promote socio-economic period 2020-2030
1. Coordinate synchronously policies of innovation in capacity development for officials of ethnic minorities
Besides coordination at ministerial level, the advisory mechanism of expertise is an important aspect of coordinating creative innovation policies to develop the capacity of ethnic minority officials. The tool of policy forecasting helps to achieve goal and can contribute to promoting a comprehensive vision that underpins the overall coordination process. There are also other tools to develop research proposals, organize roundtables, conferences, seminars, etc.
The trend of ethnic minority areas in implementing the same innovation should be considered in coordination process. This requires improvements to avoid local administrative and local centralized mechanisms. [6]
There are three issues of coordination under concern for the current renovation policy of the Vietnamese government to develop ethnic minority officials’ capacity: (1) Coordination in the innovation policy analysis to find out aspects of policies that affect the capacity of ethnic minority officials; (2) Coordinate in planning innovation policies to have long-term plans and strategies for training, retraining, rotation, planning, and appointment of cadres in ethnic minority areas; (3) Coordinating in the promulgation of innovative policies to ensure the timeliness and meet the requirements of socio-economic development of ethnic minority areas; (4) Collaboration in conducting innovation policies to bring about practical effects, avoiding the stereotyped implementation; Coordinating in the evaluation of innovation policies to draw experience, promptly develop, supplement and complete policies that directly affect the capacity of officials of ethnic minority areas.[6]
2. Designing the environment for the innovation capacity of officials in ethnic
Designing an innovation policy that is appropriate for developing the capacity of ethnic minority officials requires mastering the three components of the innovation ecosystem. Namely environment of innovation in work, legislation and innovation policy, these three components are sometimes referred to as the “Innovation Policy Triangle”.
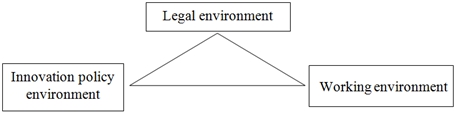
Fig. 3 – Environment for capacity development of civil servants in ethnic minority areas
Working environment:
The first side of the innovation triangle is the working environment, which includes physical, financial, and interpersonal conditions. A good working environment has many components as follows:
- The easy and effective ability of material and financial conditions to flow into innovation and profitable investment;
- The spirit of work and innovation is widespread among individuals;
- Strong e-government application, especially where administrative procedures are carried out for citizens;
- Strong management skills;
- An organizational culture that promotes competition and cooperation, as well as a degree of individual responsibility.
Legal environment: The second side of the innovation triangle is the legal environment, which creates the possibility of an appropriate overall institutional framework that facilitates innovation organizations, Including:
- An open and competitive political-administrative system that motivates ethnic minority cadres in the countryside to innovate through competition;
- Legal regulations for officials in ethnic minority areas need to be appropriate, transparent and based on efficiency standards;
- Limited regulations for a digital economy do not undermine innovation and apply digitization widely;
The legal process should be transparent and based on the rules of law;
- Public procurement should be based on performance standards as well as open and fair competition;
- Protection of intellectual property rights enables innovative innovation officials to earn income.
- How to improve the quality of legal regulations on officials operation in ethnic minority areas as well as eliminate unnecessary burdens that hinder the development of the capacity of officials in ethnic minority areas.
Innovation policy environment: The third side of the innovation triangle is a healthy innovation policy environment. While cadres are the key to innovation, the lack of an effective innovation policy will unease the competency of the staff. A strong innovation policy environment will support innovation consolidation blocks. This aspect includes:
- Support for job improvement;
- Professional enhancement support;
- Supportive digital infrastructure (such as smart networks, broadband, medical IT, intelligent transportation systems, e-government, …);
- Supportive provision of public services to promote modernization and increase labor productivity;
- Promote effective training, retraining and improvement of skills, especially leadership, management and administrative skills, attracting highly skilled staff.
- Policy makers and analysts all acknowledge that financial difficulty for innovation identically common, especially in ethnic minority and mountainous areas. In the last two decades, many countries have sought different policy measures to supplement funding to serve the capacity of innovation for ethnic minority officials from the private sector.
3. Enhancing the dissemination of information and disseminating new knowledge through domestic and foreign cooperation and training policies
a) Cooperation between science and professional activities
Successful innovation depends on the creation of initiatives and knowledge, which depend on the existence of a diverse and solid scientific foundation with modern research facilities. However, the view that links knowledge producers and technology with users (who convert this knowledge and technology into innovative products, processes and services) follows a linear process no longer exists. Knowledge creation, transfer and absorption are changing from a linear process to a “non-linear,” non-linear and known process approach (where knowledge transfer takes place out non-stop and bidirectional) [7].
b) The creative innovation policy through joint research (academic and office areas)
Central and local universities / research institutes and officials of state-owned ethnic minority organizations working together to research a project / issue at the same time will serve many purposes. Firstly, by participating actively in the project in a certain field, ethnic minority officials will gain the knowledge they need to be able to understand and assimilate discoveries from others, from which they will apply into practice to bring higher work efficiency. Second, universities / research institutes gain practical knowledge and experience, know how to solve problems that are posed in reality. In addition, the government reduces the amount of budget needed to invest in the social reality [7].
c) Policy on staff rotation between ethnic minority and mountainous areas with each other and between central and local levels
Rotating cadres in ethnic minority areas is a vital policy measure. This policy measure aims to transfer knowledge through the flow of officials of ethnic minority areas. Staff turnover is one of the important measures to promote learning among organizations as well as to spread knowledge and technology across a country.
d) Establishing and developing an innovation culture
The culture of innovation plays an important role as a channel to promote management technology transfer, job creation, growth and innovation. The policy measures to promote the creation and development of creative culture are necessary and important in organizations in ethnic minority areas.
e) Improve knowledge-synthesizing capacity through training and fostering policies
Improving the capacity to absorb knowledge and technology is an aspect of developing capacity of officials in ethnic minority areas. Collaboration for work is also in demand although this does not necessarily depend on the strong relationships that are taking place between the academic and the working sectors.
g) Raise awareness and use innovative management techniques
Innovative management techniques have a role in promoting the link between technology and work efficiency and motivating officials in ethnic minority areas to accept the perspectives. Besides, the role of International standard organization (ISO) certification, Analysis and Critical Control Point System (HACCP), Quantity Surveyor (QS), etc… is also crucial for officials in using ISO in quality management [9].
4. Designing a policy of developing the source of ethnic minority officials for innovation and a spirit of innovation
Strengthening the source of officials in ethnic minority areas for creative innovation in general and professional innovation in particular is extremely essential in the design and implementation of innovation policies. These policy measures may be conducted through:
- Improve the training system, strengthen training programs, and develop the source of professional ethnic minority staff for innovation;
- Develop a sense of responsibility and a responsible person.
Not only policy makers but also researchers on the capacity of ethnic minority officials are also interested in this issue. The sense of responsibility is seen as an engine to promote dynamism and innovation of political system in ethnic minority areas leading to socio-economic growth.
People with a sense of responsibility are considered creators of instability and innovative destruction and are innovators. In other words, the responsible person is an individual who comes up with new ideas and implements them but does not guarantee the certainty of the results. This means responsible individuals are the creators of new products, new ways of working, new organizational plans and new combinations of State and people.
IV. Conclusions and recommendations
Vietnam entered the period of international integration and accelerated industrialization and modernization of the country, so it needs to fully recognize the significance and complex properties of innovative capacity of officials in ethnic minority areas as well as be comprehensively aware of the important meaning and complicated nature of the issue of officials in ethnic minority areas.There are various newly-emerging issues, requiring a system of theoretical views and proper research methods for capacity development of officials in ethnic minority areas and a theoretical framework to evaluate innovation capacity of officials and to make long-term innovation policies. However, Vietnam’s innovation policies on capacity of officials in ethnic minority region are still in the shortage of innovation policies towards capacity development of officials including those aiming to attract, recruit, assign, train-retrain, appoint and respect talents for ethnic minority areas. Innovative policies to enhance the capacity of officials in ethnic minority areas, promote regional socio-economic growth in our country should be developed on the basis of: 1) Creating a consensus on the concept of initiative created in the process of formulating innovative policies to improve the capacity of officials in ethnic minority areas to promote regional socio-economic development; 2) Selecting key actors in the innovation system, the role of Ethnic Committee policy council, the voices of officials in ethnic minority areas; 3) Protecting ideas and brightening initiatives of officials in ethnic minority areas can form a driving force for reform, innovation and adjustment in the current intellectual property law system; 4) Enhancing financial sources for officials in ethnic minority areas to be innovative and creative; Establishing the best mechanism to attract talents to ethnic minority areas; 5) Priority policies are needed to support the capacity to acquire knowledge, science and technology for officials in ethnic minority areas in the fastest and most effective way; 6) Enhancing the role and tasks of organizations that create resources for ethnic minority people in the innovation system, these tasks should be implemented, coordinated and closely monitored; 7) Enhancing the capacity and level of technology and knowledge distribution of domestic research and development institutes for capacity building of officials in ethnic minority areas; 8) Developing intermediary institutions to monitor the formation of capacity of ethnic minority most effectively; 9) Developing a policy of appointment of prestigious ethnic minority people is really an appropriate approach due to the weakness of the internal potential of officials in ethnic minority areas; 10) Building a network of policy makers in the political system, a network of Party leaders, the governing bodies and the people to increase awareness and apply skills and innovation management techniques for officials in ethnic minority areas; 11) A diverse combination of policies in all areas related to skills, scientific research, information communication and technology, tax policies, commerce, intellectual property, public procurement, standards and regulations in a unified manner designed to improve the capacity of officials in ethnic minority areas by innovation; 12) Renewing the process of managing cadres from attracting, recruiting, appointing, training, retraining, organizing, inspecting, evaluating, commending and discipline officials of ethnic minority areas with the purpose of influencing the process of creating innovation capacity for better performance.
| Финансирование
Статья является результатом исследований в рамках национальной научной темы: «Поиск решений для улучшения способности представителей этнических меньшинств соответствовать требованиям международной интеграции, индустриализации и модернизации» код CTDT.25.17/16-20. |
Funding
The article is a research result of a national scientific topic: “Researching solutions to improve the capacity of ethnic minority officials to meet the requirements of international integration and industrialization and modernization” code CTDT.25.17/16-20. |
| Конфликт интересов
Не указан. |
Conflict of Interest
None declared. |
Список литературы / References
- Committee for Ethnic Minorities (2011) Joint Circular No. 05/2011/ TTLT-UBDT-BTC
- Government on ethnic affairs (2011). Decree No. 05/2011/ND-CP dated January 14, 2011
- OECD (2011), OECD Science, Technology and Industry Scoreboard : Innovation and Growth in Knowledge Economies (Paris: OECD, 2011),
- Peter J. Klenow and Andrés Rodríguez-Clare,(1997) “The Neoclassical Revival in Growth Economics: Has It Gone Too Far?” NBER Macroeconomics Annual (1997): 73-103
- The Government of Vietnam (2020), promulgated Resolution No. 12 / NQ-CP on February 15, 2020 on the implementation of Resolution No. 88/2019 / QH14 dated November 18, 2019 of the National Assembly on approving the Proposal master plan for socio-economic development of ethnic minority and mountainous areas in the 2021-2030 period.
- The Government of Vietnam Resolution (2020) 12/ NQ-CP 2020 implements the Project on socio-economic development of ethnic minorities and mountainous areas.
- Tran Cong Yen The basic knowledge of innovation , Science & Technology Publishing House, 2012, Hanoi
- Vietnam National Assembly The Law on Cadres and Civil Servants of Vietnam, 2008
- Vu Van Khiem Building a framework of innovation capacity for businesses in accordance with the reality in Vietnam / Vu Van Khiem, Ho The Nam Phuong, Bui Tien Dung // 2018, Journal of Science and Technology Management and Science No. 2/2018



